Building a New Venture Team -- Getting Financing or Funding (Session 15-16) [Week GSLC 2]
Building a New-Venture Team
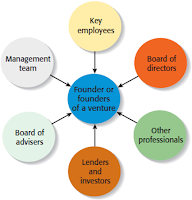
New Venture Team
-
Is
the group of founders, key employees, and advisers that move a new venture from
an idea to a fully functioning firm.
-
Usually,
the team doesn’t come together all at once.
Instead, it is built as the new firm can afford to hire additional
personnel.
-
The
team also involves more than paid employees.
o
Many
firms have boards of directors, boards of advisers, and professionals on whom
they rely for direction and advice.
Liabilities
of Newness
-
New
ventures have a high propensity to fail.
-
The
high failure rate is due in part to liabilities of newness, which refers to the
fact that new companies often falter because the people involved can’t adjust
fast enough to their new roles and because the firm lacks a track record of
success.
-
Assembling
a talented and experienced management team is one path that firms can take to
overcome these limitations.
Separate
Elements of a New Venture Team
The Founder
or Founders
-
The
characteristics of the founder or founders of a firm and their early decisions
have a significant impact on the manner in which the new venture team takes
shape.
-
Studies
have shown that 50% to 70% of all new ventures are started by more than one
individual.
-
It
is believed that new ventures that are started by a team rather than a single
individual have an advantage.
Factors That May
Contribute to a Founders’ Success
• Firm started by a team
• Higher education
• Prior entrepreneurial experience
• Relevant industry experience
• The ability to “network” effectively
Factors
that Contribute to a Founder or Founders’ Success
Start-ups started by a
team can provide greater resources, a broader diversity of viewpoints, and a broader
array of other positive attributes than ventures started by individuals.
Entrepreneurial skills
are enhanced through higher education.
Founders familiar with
the entrepreneurial process are more likely to avoid costly mistakes than
founders without similar experience.
Founders with relevant
industry experience are more likely to have:
• Better
established professional networks
• More applicable marketing and
management skills
Founders with broad social and
professional networks have potential access to additional know-how, capital,
and customer referrals.
Recruiting
and Selecting Key Employees
-
Startups
vary in terms of how quickly they need to add personnel.
-
In
some instances, the founders will work alone for a period of time. In other instances, employees are hired
immediately.
-
A
skills profile is a chart that depicts the most important skills that
are needed and where skills gaps exist in a new firm.
The Roles
of the Board of the Directors
-
If
a new venture organizes as a corporation, it is legally required to have a
board of directors.
-
A
board of directors is a panel of individuals who are elected by a corporation’s
shareholders to oversee the management of the firm.
-
A
board is typically made up of both inside directors and outside directors.
o
An
inside director is a person who is also an officer of the firm.
o
An
outside director is someone who is not employed by the firm.
-
A
board of directors has three formal responsibilities.
o
Appoint
the officers of the firm.
o
Declare
dividends.
o
Oversee
the affairs of the corporation
- Meet
three to four times a year.
-
New
ventures are more likely to pay their board members in company stock or ask
them to service on a voluntary basis rather than pay a cash honorarium.
Rounding out the Team: The Role of Professional Advisors
-
A
board of advisors is a panel of experts who are asked by a firm’s managers to
provide counsel and advice on an ongoing basis.
-
Unlike
a board of directors, an advisory board possesses no legal responsibility for
the firm and gives nonbinding advice.
-
An
advisory board can be established for general purposes or can be set up to
address a specific issue or need.
-
Many
people are more willing to serve on a company’s board of advisors than its
board of directors because it requires less time and there is no potential
legal liability involved.
-
Like
the members of a board of directors, the members of a company’s board of
advisors provide guidance and lend credibility to the firm.
-
Advisors
will become disillusioned if they don’t play a meaningful role in the firm’s
development and growth.
-
A
firm should look for board members who are compatible and complement one
another in terms of experience and expertise.
-
When
inviting people to serve on its board of advisors, a company should carefully
spell out to the individuals involved the rules in terms of access to
confidential information.
-
Lenders
and investors have a vested interest in the companies they finance, often
causing them to become very involved in helping the firms they fund.
-
Like
the other non-employee members of a firm’s new venture team, lenders and
investors help new firms by providing guidance and lending advice.
-
In
addition, a firm’s lenders and investors assume the natural role of providing
financial oversight.
Ways Lenders and Investors Add
Value to Entrepreneurial Firm
-
Help
identify and recruit key management personnel
-
Provide
insight into the markets that the new venture plans to enter
-
Help
the venture fine-tune its business model
-
Serve
as a sounding board for new ideas
-
Provide
introductions to additional sources of capital
-
Serve
on the new venture’s board of directors or board of advisors
-
Recruit
customers
-
Help
to arrange business partnerships
-
Serve
on the board of directors or board of advisors
-
Provide
a sense of stability and calm
Other
Professionals
-
The
other professionals that make up a firm’s new venture team include attorneys,
accountants, and business consultants.
-
A
business consultant is an individual who gives professional or expert advice.
-
Business
consultants fall into two categories: paid consultants and consultants who are
available for free or at a reduced rate through a nonprofit of governmental
agency.
GETTING
FINANCING OR FUNDING
The Importance of Getting Financing or Funding
Ø
Few
people deal with the process of raising investment capital until they need to
raise capital for their own firm.
o
As
a result, many entrepreneurs go about the task of raising capital haphazardly
because they lack experience in this area.
Ø
There are three reason most new ventures need to
raise money during their early life
o
Three three reasons are shown on the following
slide
Alternatives
for Raising Money for a New Venture
Source of
Personal Financing
Ø
The
vast majority of founders contribute personal funds, along with sweat equity,
to their ventures.
o
Sweat
equity represents the value of the time and effort that a founder puts into a
new venture.
Ø
Friends and family are the second source of
funds for many new ventures
Ø
A
third source of seed money for a new venture is referred to as bootstrapping.
Ø
Bootstrapping
is finding ways to avoid the need for external financing or funding through
creativity, ingenuity, thriftiness, cost-cutting, or any means necessary.
Ø
Many
entrepreneurs bootstrap out of necessity.
Preparing
to Raise Debt or Equity Financing
Step 1 → Determine precisely how much money is needed
Step 2 → Determine the type of financing or funding that is the most
appropriate
Step 3 → Develop a strategy for engaging potential investors or
bankers
Two Most Common Alternatives:
-
Equity Funding → Means exchanging partial ownership
in a firm, usually in the form of stock, for funding
-
Debt Financing → is getting a loan
Preparing An Elevator Speech
Purpose:
-
An
elevator speech is a brief,
-
carefully constructed statement
-
that outlines the merits of a
-
business opportunity.
-
There are many occasions when a
-
carefully constructed elevator
-
speech might come in handy.
-
Most elevator speeches are 45
-
seconds to 2 minutes long.
Sources of
Equity Funding
Business
Angels
-
Are
individuals who invest their personal capital directly in start-ups.
-
The
prototypical business angel is about 50 years old, has high income and wealth,
is well educated, has succeeded as an entrepreneur, and is interested in the
startup process.
-
The
number of angel investors in the U.S. has increased dramatically over the past
decade.
-
Business
angels are valuable because of their willingness to make relatively small
investments.
o
These
investors generally invest between $10,000 and $500,000 in a single company.
o
Are
looking for companies that have the potential to grow between 30% to 40% per
year.
-
Business
angels are difficult to find.
Venture
Capital
-
Is
money that is invested by venture-capital firms in start-ups and small
businesses with exceptional growth potential.
-
There
are about 650 venture-capital firms in the U.S. that provide funding to about
2,600 firms per year.
o
Venture-capital
firms are limited partnerships of money managers who raise money in “funds” to
invest in start-ups and growing firms.
o
The
funds, or pool of money, are raised from wealthy individuals, pension plans,
university endowments, foreign investors, and similar sources.
o
A
typical fund is $75 million to $200 million and invests in 20 to 30 companies
over a three- to five-year period.
-
Venture
capital firms fund very few entrepreneurial firms in comparison to business
angels.
o
Many
entrepreneurs get discouraged when they are repeatedly rejected for venture
capital funding, even though they may have an excellent business plan.
o
Venture
capitalists are looking for the “home run” and so reject the majority of the
proposals they consider.
o
Still,
for the firms that qualify, venture capital is a viable alternative for equity
funding.
-
An
important part of obtaining venture-capital funding is going through the due
diligence process.
-
Venture
capitalists invest money in start-ups in “stages,” meaning that not all the
money that is invested is disbursed at the same time.
-
Some
venture capitalists also specialize in certain “stages” of funding.
Initial
Public Offering
-
An
initial public offering (IPO) is a company’s first sale of stock to the
public. When a company goes public, its
stock is traded on one of the major stock exchanges.
-
Most
entrepreneurial firms that go public trade on the NASDAQ, which is weighted
heavily toward technology, biotech, and small-company stocks.
-
An
IPO is an important milestone for a firm.
Typically, a firm is not able to go public until it has demonstrated
that it is viable and has a bright future.
Reasons
that Motivate Firms to Go Public:
-
Reason 1 → Is a way to
raise equity capital to fund current and future operations.
-
Reason 2 → Raises a
firm’s public profile, making it easier to attract high-quality customers and
business partners.
-
Reason 3 → Is a liquidity
event that provides a means for a company’s investors to recoup their
investments.
-
Reason 4 → Creates a form
of currency that can be used to grow the company via acquisitions.
Sources of
Debt Financing
-
Historically,
commercial banks have not been viewed as a practical sources of financing for
start-up firms.
-
This
sentiment is not a knock against banks; it is just that banks are risk adverse,
and financing start-ups is a risky business.
o
Banks
are interested in firms that have a strong cash flow, low leverage, audited
financials, good management, and a healthy balance sheet.
-
The
SBA Guaranteed Loan Program
o
Approximately
50% of the 9,000 banks in the U.S. participate in the SBA Guaranteed Loan
Program.
o
The
program operates through private-sector lenders who provide loans that are
guaranteed by the SBA.
o
The
loans are for small businesses that are not able to obtain credit elsewhere.
-
The
7(A) Loan Guaranty Program
o
The
most notable SBA program available to small businesses.
-
Almost
all small businesses are eligible to apply for an SBA guaranteed loan.
-
The
SBA can guarantee as much as 85% on loans up to $150,000 and 75% on loans over
$150,000.
-
An
SBA guaranteed loan can be used for almost any legitimate business purpose.
-
Since
its inception, the SBA has helped make $280 billion in loans to nearly 1.3
million businesses.
Other
Sources of Debt Financing
-
Friends
and Family
-
Credit
Cards
o
Should
be used sparingly.
-
Peer-to-Peer
Lending Networks
o
Examples
include Propser.com and Zopa.com.
-
Organizations
that Lend Money to Specific Groups
o
An
example is Count Me In, an organization that provides loans of $500 to $10,000
to women starting or growing a business.
Creative
Sources of Financing or Funding
Leasing
-
A
lease is a written agreement in which the owner of a piece of property allows
an individual or business to use the property for a specified period of time in
exchange for payments.
-
The
major advantage of leasing is that it enables a company to acquire the use of
assets with very little or no down payment.
-
Most
leases involve a modest down payment and monthly payments during the duration
of the lease.
-
At
the end of an equipment lease, the new venture typically has the option to stop
using the equipment, purchase it for fair market value, or renew the
lease.
-
Leasing
is almost always more expensive than paying cash for an item, so most
entrepreneurs think of leasing as an alternative to equity or debt financing.
SBIR and STTR Grants
-
The
Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) and the Small Business Technology
Transfer (STTR) programs are two important sources of early-stage funding for
technology firms.
-
These
programs provide cash grants to entrepreneurs who are working on projects in
specific areas.
o
The
main difference between the SBIR and the STTR programs is that the STTR program
requires the participation of researchers working at universities or other
research institutions.
-
The
SBIR Program is a competitive grant program that provides over $1 billion per
year to small businesses in early-stage and development projects.
-
Each
year, 11 federal departments and agencies are required by the SBIR to reserve a
portion of their R&D funds for awards to small businesses.
-
Guidelines
for how to apply for the grants are provided on each agency’s Web site.
-
The
SBIR is a three phase program, meaning that firms that qualify have the
potential to receive more than one grant to fund a particular proposal.
-
Historically,
less than 15% of all phase I proposals are funded. The payoff for successful proposals, however,
is high.
o
The
money is essentially free. It is a
grant, meaning that it doesn’t have to be paid back and no equity in the firm
is at stake.
o
The
small business receiving the grant also retains the rights to any intellectual
property generated as the result of the grant initiative.
Other Grant
Programs
-
There
are a limited number of grants programs available.
-
Getting
grants takes a little detective work.
-
Granting
agencies are low key, and must be sought out.
-
The
federal government has grant programs beyond the SBIR and STTR programs.
-
Be
careful of grant-related scams.
Strategic
Partners
-
Strategic
partners are another source of capital for new ventures.
-
Many
partnerships are formed to share the costs of product or service development,
to gain access to particular resources, or to facilitate speed to market.
Older established firms benefit by partnering
with young entrepreneurial firms by gaining access to their creative ideas and
entrepreneurial spirit.
GETTING
FINANCING OR FUNDING
The Importance of Getting Financing or Funding
Ø
Few
people deal with the process of raising investment capital until they need to
raise capital for their own firm.
o
As
a result, many entrepreneurs go about the task of raising capital haphazardly
because they lack experience in this area.
Ø
There are three reason most new ventures need to
raise money during their early life
o
Three three reasons are shown on the following
slide
Alternatives
for Raising Money for a New Venture
Source of
Personal Financing
Ø
The
vast majority of founders contribute personal funds, along with sweat equity,
to their ventures.
o
Sweat
equity represents the value of the time and effort that a founder puts into a
new venture.
Ø
Friends and family are the second source of
funds for many new ventures
Ø
A
third source of seed money for a new venture is referred to as bootstrapping.
Ø
Bootstrapping
is finding ways to avoid the need for external financing or funding through
creativity, ingenuity, thriftiness, cost-cutting, or any means necessary.
Ø
Many
entrepreneurs bootstrap out of necessity.
Preparing
to Raise Debt or Equity Financing
Step 1 → Determine precisely how much money is needed
Step 2 → Determine the type of financing or funding that is the most
appropriate
Step 3 → Develop a strategy for engaging potential investors or
bankers
Two Most Common Alternatives:
-
Equity Funding → Means exchanging partial ownership
in a firm, usually in the form of stock, for funding
-
Debt Financing → is getting a loan
Preparing An Elevator Speech
Purpose:
-
An
elevator speech is a brief,
-
carefully constructed statement
-
that outlines the merits of a
-
business opportunity.
-
There are many occasions when a
-
carefully constructed elevator
-
speech might come in handy.
-
Most elevator speeches are 45
-
seconds to 2 minutes long.
Sources of
Equity Funding
Business
Angels
-
Are
individuals who invest their personal capital directly in start-ups.
-
The
prototypical business angel is about 50 years old, has high income and wealth,
is well educated, has succeeded as an entrepreneur, and is interested in the
startup process.
-
The
number of angel investors in the U.S. has increased dramatically over the past
decade.
-
Business
angels are valuable because of their willingness to make relatively small
investments.
o
These
investors generally invest between $10,000 and $500,000 in a single company.
o
Are
looking for companies that have the potential to grow between 30% to 40% per
year.
-
Business
angels are difficult to find.
Venture
Capital
-
Is
money that is invested by venture-capital firms in start-ups and small
businesses with exceptional growth potential.
-
There
are about 650 venture-capital firms in the U.S. that provide funding to about
2,600 firms per year.
o
Venture-capital
firms are limited partnerships of money managers who raise money in “funds” to
invest in start-ups and growing firms.
o
The
funds, or pool of money, are raised from wealthy individuals, pension plans,
university endowments, foreign investors, and similar sources.
o
A
typical fund is $75 million to $200 million and invests in 20 to 30 companies
over a three- to five-year period.
-
Venture
capital firms fund very few entrepreneurial firms in comparison to business
angels.
o
Many
entrepreneurs get discouraged when they are repeatedly rejected for venture
capital funding, even though they may have an excellent business plan.
o
Venture
capitalists are looking for the “home run” and so reject the majority of the
proposals they consider.
o
Still,
for the firms that qualify, venture capital is a viable alternative for equity
funding.
-
An
important part of obtaining venture-capital funding is going through the due
diligence process.
-
Venture
capitalists invest money in start-ups in “stages,” meaning that not all the
money that is invested is disbursed at the same time.
-
Some
venture capitalists also specialize in certain “stages” of funding.
Initial
Public Offering
-
An
initial public offering (IPO) is a company’s first sale of stock to the
public. When a company goes public, its
stock is traded on one of the major stock exchanges.
-
Most
entrepreneurial firms that go public trade on the NASDAQ, which is weighted
heavily toward technology, biotech, and small-company stocks.
-
An
IPO is an important milestone for a firm.
Typically, a firm is not able to go public until it has demonstrated
that it is viable and has a bright future.
Reasons
that Motivate Firms to Go Public:
-
Reason 1 → Is a way to
raise equity capital to fund current and future operations.
-
Reason 2 → Raises a
firm’s public profile, making it easier to attract high-quality customers and
business partners.
-
Reason 3 → Is a liquidity
event that provides a means for a company’s investors to recoup their
investments.
-
Reason 4 → Creates a form
of currency that can be used to grow the company via acquisitions.
Sources of
Debt Financing
-
Historically,
commercial banks have not been viewed as a practical sources of financing for
start-up firms.
-
This
sentiment is not a knock against banks; it is just that banks are risk adverse,
and financing start-ups is a risky business.
o
Banks
are interested in firms that have a strong cash flow, low leverage, audited
financials, good management, and a healthy balance sheet.
-
The
SBA Guaranteed Loan Program
o
Approximately
50% of the 9,000 banks in the U.S. participate in the SBA Guaranteed Loan
Program.
o
The
program operates through private-sector lenders who provide loans that are
guaranteed by the SBA.
o
The
loans are for small businesses that are not able to obtain credit elsewhere.
-
The
7(A) Loan Guaranty Program
o
The
most notable SBA program available to small businesses.
-
Almost
all small businesses are eligible to apply for an SBA guaranteed loan.
-
The
SBA can guarantee as much as 85% on loans up to $150,000 and 75% on loans over
$150,000.
-
An
SBA guaranteed loan can be used for almost any legitimate business purpose.
-
Since
its inception, the SBA has helped make $280 billion in loans to nearly 1.3
million businesses.
Other
Sources of Debt Financing
-
Friends
and Family
-
Credit
Cards
o
Should
be used sparingly.
-
Peer-to-Peer
Lending Networks
o
Examples
include Propser.com and Zopa.com.
-
Organizations
that Lend Money to Specific Groups
o
An
example is Count Me In, an organization that provides loans of $500 to $10,000
to women starting or growing a business.
Creative
Sources of Financing or Funding
Leasing
-
A
lease is a written agreement in which the owner of a piece of property allows
an individual or business to use the property for a specified period of time in
exchange for payments.
-
The
major advantage of leasing is that it enables a company to acquire the use of
assets with very little or no down payment.
-
Most
leases involve a modest down payment and monthly payments during the duration
of the lease.
-
At
the end of an equipment lease, the new venture typically has the option to stop
using the equipment, purchase it for fair market value, or renew the
lease.
-
Leasing
is almost always more expensive than paying cash for an item, so most
entrepreneurs think of leasing as an alternative to equity or debt financing.
SBIR and STTR Grants
-
The
Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) and the Small Business Technology
Transfer (STTR) programs are two important sources of early-stage funding for
technology firms.
-
These
programs provide cash grants to entrepreneurs who are working on projects in
specific areas.
o
The
main difference between the SBIR and the STTR programs is that the STTR program
requires the participation of researchers working at universities or other
research institutions.
-
The
SBIR Program is a competitive grant program that provides over $1 billion per
year to small businesses in early-stage and development projects.
-
Each
year, 11 federal departments and agencies are required by the SBIR to reserve a
portion of their R&D funds for awards to small businesses.
-
Guidelines
for how to apply for the grants are provided on each agency’s Web site.
-
The
SBIR is a three phase program, meaning that firms that qualify have the
potential to receive more than one grant to fund a particular proposal.
-
Historically,
less than 15% of all phase I proposals are funded. The payoff for successful proposals, however,
is high.
o
The
money is essentially free. It is a
grant, meaning that it doesn’t have to be paid back and no equity in the firm
is at stake.
o
The
small business receiving the grant also retains the rights to any intellectual
property generated as the result of the grant initiative.
Other Grant
Programs
-
There
are a limited number of grants programs available.
-
Getting
grants takes a little detective work.
-
Granting
agencies are low key, and must be sought out.
-
The
federal government has grant programs beyond the SBIR and STTR programs.
-
Be
careful of grant-related scams.
Strategic
Partners
-
Strategic
partners are another source of capital for new ventures.
-
Many
partnerships are formed to share the costs of product or service development,
to gain access to particular resources, or to facilitate speed to market.
Older established firms benefit by partnering
with young entrepreneurial firms by gaining access to their creative ideas and
entrepreneurial spirit.

Komentar
Posting Komentar